 Calcutta, Day of the population of the Earth (World Population Day), on July, 11th, 2011 . It is supposed that by 2020 India will overtake China on population. A picture from: Science. 2011 V. 333. P. 538 Calcutta, Day of the population of the Earth (World Population Day), on July, 11th, 2011 . It is supposed that by 2020 India will overtake China on population. A picture from: Science. 2011 V. 333. P. 538 Number of the population quickly grows now. Thus the centre of growth from Europe and the North America has moved to developing countries of South East Asia and Africa. The forecast for the future depends on that, how fast in these countries birth rate will decrease. At the different accepted values of factor fertility (numbers of children born for life by one mother) it is expected that by 2100 on the Earth there will be from 6,1 to 15,8 mlrd a person. In 2011 the aggregate number of people on a planet has reached 7 billion. This to a certain extent sign figure became an occasion to occurrence in magazine Science of some the publications analyzing a current situation and containing forecasts for the future. During at least 2,4 million years representatives of sort Homo remained collectors, but in the beginning Holocene in several different places (in East Mediterranean, on New Guinea, in Ethiopia, in the north and in the south of China, in east part of the North America and in the South America) the primitive agriculture began to appear. Chronologically it occurred in wide enough time interval — from 11 500 to 3500 years ago. Most likely, number Homo sapiens at the beginning of agriculture made about 6 million. For the past since then 11 thousand years it has increased in 1200 times!
Transition from a hunting and collecting epoch to agriculture name «Neolithic revolution». Its basic result — essential increase in number of people which could live from the same territory. So, if collecting and hunting could support existence no more than 0,05 persons on 1 кm2 the modern agriculture can with 1 кm2 the cultivated earth to provide livelihood of 54 persons, and by 2050 this figure will reach, probably, 70–80 persons. About that number of people began to grow quickly after «Neolithic revolutions», the analysis of the bone rests in ancient burial places testifies. Among the found out skeletons the share of children and teenagers (from 5 till 19 years) has sharply increased, on what Jean-Pierre Boke-Appel (Jean-Pierre Bocquet-Appel) from the National centre of scientific researches of France specially pays attention. Similar shift of age structure in populations of the ancient person testifies to essential increase of birth rate. And though death rate still remained high, populations nevertheless began to grow faster. Noted change in the ratio birth rate and death rate name «Neolithic demographic transition». To some extent it mirror to "modern demographic transition» for which fast decrease in death rate (first of all infantile) is characteristic at preservation of high birth rate (which only then will start to decrease).  Fig. 1. At the left: growth of the population since prehistoric times to the present and the forecast for 2024 . This year, in 13 years, number of people on the Earth will reach 8 billion. Red colour about the schedule specifies years when population of the Earth reached the next billion. On the right: population growth for last 60 years and the forecast for 2050 at an assumption of average estimations of birth rate and death rate. Moderated (and, probably, the most probable forecast) — 9,3 billion the share of India, China, the African countries, less developed countries of other continents, more developed countries Is shown. From: Science V. 333. P. 540. The given Organizations of the incorporated nations Fig. 1. At the left: growth of the population since prehistoric times to the present and the forecast for 2024 . This year, in 13 years, number of people on the Earth will reach 8 billion. Red colour about the schedule specifies years when population of the Earth reached the next billion. On the right: population growth for last 60 years and the forecast for 2050 at an assumption of average estimations of birth rate and death rate. Moderated (and, probably, the most probable forecast) — 9,3 billion the share of India, China, the African countries, less developed countries of other continents, more developed countries Is shown. From: Science V. 333. P. 540. The given Organizations of the incorporated nations
In different places in Northern hemisphere «Neolithic demographic transition» was observed approximately through one thousand years after occurrence in the given area of agriculture. Despite high birth rate, the aggregate number of people on the Earth grew slowly enough. First billion has been reached approximately by 1800 , and 125 years were required as early as to reach two billions. However that number of the population has increased from three to seven billions, 50 years (fig. 1) have sufficed.  Fig. 2. Above: growth rate changes (in %) the population with 1950 for 2010 . The maximum had for 1965-1970 . After that rates of a gain of the population steadily decreased. Below: change fertility with 1950 for 2010 . An average curve — for the whole world. The top (brown) curve — less developed countries (except for China). The bottom (yellow) curve — more developed countries. From: Science V. 333. P. 541. The given Organizations of the incorporated nations Fig. 2. Above: growth rate changes (in %) the population with 1950 for 2010 . The maximum had for 1965-1970 . After that rates of a gain of the population steadily decreased. Below: change fertility with 1950 for 2010 . An average curve — for the whole world. The top (brown) curve — less developed countries (except for China). The bottom (yellow) curve — more developed countries. From: Science V. 333. P. 541. The given Organizations of the incorporated nations
As David Blum (David E writes in the review. Bloom) from the Harward university (USA) it is expected that in 2011 on light will appear 135 million persons, and will die approximately 57 million. Accordingly, the pure gain will make 78 million persons. Supervision over speed of an increase in population (in % from an aggregate number for a year) have shown that the maximum value (about 2 %) was necessary for 1965-70th years (fig. 2). It just years of the demographic transition occurring in developing countries: decrease in children's death rate at preservation of high birth rate (fig. 3). But since then rate of a gain in regular intervals decreases and now makes hardly more than 1 %.  Fig. 3. The scheme of demographic transition: increase of level of public health services sharply reduces death rate (death rate — a brown line), first of all infantile, but birth rate (birh rate — a green line) during some time remains still high. Therefore also speed популяционного growth (it is shown by an arrow) sharply increases. During such period also there is a fast growth of the population. Then birth rate decreases also. Balance is established at lower level. From: Science. 2011 V. 333. P. 562–569
Fig. 3. The scheme of demographic transition: increase of level of public health services sharply reduces death rate (death rate — a brown line), first of all infantile, but birth rate (birh rate — a green line) during some time remains still high. Therefore also speed популяционного growth (it is shown by an arrow) sharply increases. During such period also there is a fast growth of the population. Then birth rate decreases also. Balance is established at lower level. From: Science. 2011 V. 333. P. 562–569
Immediate cause of decrease in rate of a gain of population — birth rate reduction which usually judge on size fertility (fig. 2.), that is to average quantity of children born by one woman for the life. In a domestic demography this indicator name also total factor of birth rate as for each concrete year it pays off as the sum age-specific birth rate factors (whence and the name). It corresponds to average of children which would be given birth by the woman of hypothetical generation for the life under condition of preservation in population of the same distribution of birth rate on age which was observed in the given region in the given year.
Despite the general falling fertility over the last 50 years , the different countries very strongly differ on this indicator (see a card on fig. 4). High level fertility — on the average , more than 5 children on one woman — remains in the countries of Africa, especially that lie to the south from Sahara (for example, 5,3 in Angola and 7,0 in Nigeria). In the Asian countries fertility as a whole more low (2,6 in India, 1,6 in China, 1,4 in Japan, but 6,2 in Afghanistan). In the countries of Europe and in Russia total factor of birth rate very low — from 1,1 to 2,2. (For maintenance of constant number of population under condition of low death rate observed now it is necessary, that it was at least 2,1–2,2).  Fig. 4. Size distribution fertility (total factor of birth rate) on all globe for 2010 . The given factor is better reflects speed of birth rate. It pays off as average of children which would be given birth by the woman for the life if factors age-specific birth rate and death rate remained same as they were in the given year. It is well visible that the highest birth rate in the countries of Africa and some countries of Asia, for example Afghanistan. Very low birth rate remains in the majority of the countries of Europe and in Russia. From: Science V. 333. P. 542. The given Organizations of the incorporated nations Fig. 4. Size distribution fertility (total factor of birth rate) on all globe for 2010 . The given factor is better reflects speed of birth rate. It pays off as average of children which would be given birth by the woman for the life if factors age-specific birth rate and death rate remained same as they were in the given year. It is well visible that the highest birth rate in the countries of Africa and some countries of Asia, for example Afghanistan. Very low birth rate remains in the majority of the countries of Europe and in Russia. From: Science V. 333. P. 542. The given Organizations of the incorporated nations
Certainly, serious achievement of the human civilisation which have affected a demographic situation, — this radical increase in average life expectancy. Apparently, during more average expected life expectancy at the moment of a birth made parts of history of mankind about 30 years as infantile death rate was very high. But for two decades, approximately since 1950 , average expected life expectancy (and it is the best indicator of a condition of public health services) as a whole on the world has increased approximately for 20 years. In more developed countries the increase was with 47 till 67 years, in less developed — with 41 till 67 years. As a whole on the world now average expected duration varies from 48 years in Sierra Leone till 83 years in Japan. In the developed countries of Western Europe — from 74 in Hungary till 82 years in Switzerland.
If in the majority of the countries average expected life expectancy since 1950th years all time increased, in Russia it, having reached in 1961 69 years, further did not increase, and from time to time even decreased. Small, but significant increase (especially for men) has been reached in 1986-89 thanking Gorbachev the antialcoholic company, but with its termination life expectancy began to decrease promptly, having reached a minimum in 1994 : 57 of years for men and 72 years for women. Then it has a little increased and has stiffened at level of 68 years for all population on the average . Feature of Russia — very big difference between life expectancy of men and women.
In a number of the African countries sharp increase of death rate from AIDS (and the young population becomes its victims) has led to significant reduction of life expectancy. In Zimbabwe, for example , it made 61,7 years in 1987 and only 43,2 years in 2003 though during the latest time has increased to 51,4 years. Despite successes in maintenance of life sick of AIDS, this illness still carries away set of lives. In 2009 in the world from AIDS has died 1,8 million persons that has made 3,2 % of all death for a year. 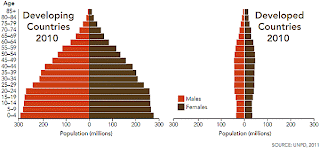 Fig. 5. Absolute number (in millions) different age groups of the population in the developing (at the left) and developed countries developing (at the left) (on the right). The data for 2010 . Age classes are allocated for 5 years. At the left — men, on the right — women. Sharp domination in developing countries of the young population — pledge of fast growth of number of the population. From: Science V. 333. P. 542. The given Organizations of the incorporated nations Fig. 5. Absolute number (in millions) different age groups of the population in the developing (at the left) and developed countries developing (at the left) (on the right). The data for 2010 . Age classes are allocated for 5 years. At the left — men, on the right — women. Sharp domination in developing countries of the young population — pledge of fast growth of number of the population. From: Science V. 333. P. 542. The given Organizations of the incorporated nations
The increase in life expectancy and presence of demographic transition ("bebi-boom" as consequence of reduction of infantile death rate) has led to serious changes of age structure. Changes in more developed countries where the numerous cohort (generated in days of high birth rate) has reached age actively working were especially radical, but will be soon already presented by a considerable quantity of the older persons needing guardianship. At the same time in developing countries the share of children and young men is still very great and the share of old men (fig. 5) is small. See dynamics of change of age structure on fig. 6 (it not model, and the real data on two groups of the countries). If in the African countries to the south of Sahara of the population of 43 % is more younger 15 years, and only 3 % have age is more senior 65 years in the countries of Europe on children and teenagers (till 15 years) 16 % of the population are necessary, and the same of 16 % are made by inhabitants is more senior 65 years.
|
 Fig. 6. Changes of age structure (a parity of number of different age classes) for group of the countries of South East Asia (A) and groups of the countries in Africa to the south of Sahara (B) during the period with 1950 for 2050 . From left to right on the bottom axis separate age classes (for 5 years) are shown. One colour allocates the data on the age structure, averaged for five years. It is well visible that in more developed countries of South East Asia as a result of birth rate decrease in 1980-h-1990th years accurately expressed shift of numerous cohorts (results of high birth rate of 1950-70th years) on more and more late age is observed, that is there is a population ageing. Birth rate all time grows in developing countries of Africa, and as a result in population more and more dominate early age. From: Science. 2011 V. 333. P. 562–569 Fig. 6. Changes of age structure (a parity of number of different age classes) for group of the countries of South East Asia (A) and groups of the countries in Africa to the south of Sahara (B) during the period with 1950 for 2050 . From left to right on the bottom axis separate age classes (for 5 years) are shown. One colour allocates the data on the age structure, averaged for five years. It is well visible that in more developed countries of South East Asia as a result of birth rate decrease in 1980-h-1990th years accurately expressed shift of numerous cohorts (results of high birth rate of 1950-70th years) on more and more late age is observed, that is there is a population ageing. Birth rate all time grows in developing countries of Africa, and as a result in population more and more dominate early age. From: Science. 2011 V. 333. P. 562–569
Similar changes of age structure have important consequences for economy as the parity of number actively working and those who is on their care changes. If to consider as the worker age from 15 till 64 years, the relation of number working to idle in the developed countries has increased with 1,24 in 1950 to 2,05 in 2011. But this relation grows in developing countries more slowly — with 1,41 to 1,89 (for the same time). In the African countries to the south of Sahara it even has decreased: with 1,22 to 1,20. The reason — preservation of high birth rate and very high number of children and teenagers. In many Asian countries economy lifting spoke partly presence of a numerous cohort of people of active working age, but in process of ageing of the population and at preservation of very low birth rate these countries in the future are threatened with the serious difficulties caused by necessity to provide life of old people.
If to start with average values of factor fertility, that, according to calculations of experts of Department of development of the United Nations, the population aggregate number will reach 9,3 mlrd by 2050 and 10,1 mlrd by 2100 . If to admit that fertility will decrease, in 2050 8,5 billion is expected only If it remains high by 2050 it is necessary to expect 10,6 billion Accordingly, the forecast for 2100 — from 6,1 to 15,8 mlrd depending on the accepted values fertility. If to speak about a point of achievement of the maximum number (peak, after which number will start to decrease), in case of low fertility it it will be reached in 2045 (8,1 mlrd), in case of high — after 2100 (15,8 mlrd).
Now most of all people lives in China (1,35 mlrd). It only slightly is lagged behind by India (1,24 mlrd) which by 2050 becomes the most populous country with an aggregate number of the population of 1,69 billion From 10 largest on population of the countries only three — the USA, Russia and Japan — concern a category developed, but by 2050 Russia will be not included any more into first ten the most occupied countries. And Nigeria which now occupies 7 place, will pass on 4.
Authors of articles in Science underline that, despite serious difficulties which the mankind in process of the population growth faces, time and again becoming alarmist predictions, in general, did not prove to be true. Changes of age structure occurring now and decrease in birth rate in process of growth of formation and well-being give to hope of overcoming of the crisis caused by too high number of people.
|
 Fig. 6. Changes of age structure (a parity of number of different age classes) for group of the countries of South East Asia (A) and groups of the countries in Africa to the south of Sahara (B) during the period with 1950 for 2050 . From left to right on the bottom axis separate age classes (for 5 years) are shown. One colour allocates the data on the age structure, averaged for five years. It is well visible that in more developed countries of South East Asia as a result of birth rate decrease in 1980-h-1990th years accurately expressed shift of numerous cohorts (results of high birth rate of 1950-70th years) on more and more late age is observed, that is there is a population ageing. Birth rate all time grows in developing countries of Africa, and as a result in population more and more dominate early age. From: Science. 2011 V. 333. P. 562–569
Fig. 6. Changes of age structure (a parity of number of different age classes) for group of the countries of South East Asia (A) and groups of the countries in Africa to the south of Sahara (B) during the period with 1950 for 2050 . From left to right on the bottom axis separate age classes (for 5 years) are shown. One colour allocates the data on the age structure, averaged for five years. It is well visible that in more developed countries of South East Asia as a result of birth rate decrease in 1980-h-1990th years accurately expressed shift of numerous cohorts (results of high birth rate of 1950-70th years) on more and more late age is observed, that is there is a population ageing. Birth rate all time grows in developing countries of Africa, and as a result in population more and more dominate early age. From: Science. 2011 V. 333. P. 562–569 





No comments:
Post a Comment